Blood Thinner Targets: What They Are and How They Work
When doctors talk about blood thinner targets, the biological mechanisms drugs act on to reduce clotting and prevent strokes or heart attacks. Also known as anticoagulant pathways, these targets are the reason some pills stop clots before they form. It’s not magic—it’s biology. Your blood naturally clots to stop bleeding after a cut. But when clots form inside arteries or veins, they can block blood flow to your heart, brain, or lungs. That’s where blood thinner targets come in: they’re the specific spots in your body’s clotting system that medications are designed to tweak.
There are a few key players here. One is warfarin, a vitamin K antagonist that slows down the production of clotting proteins in the liver. Another is aspirin, a platelet inhibitor that stops blood cells from sticking together. Then there are newer drugs like apixaban and rivaroxaban, which block a protein called Factor Xa. Each one hits a different target, and that’s why you can’t just swap them around. Mixing them without knowing how they work together can be risky. For example, if you’re on warfarin and start taking fish oil, an omega-3 supplement that mildly reduces platelet stickiness, your bleeding risk might creep up—even if you’re not taking a high dose. It’s not always obvious, and that’s why some people end up in the ER with unexpected bruising or nosebleeds.
It’s not just about pills. Things like diet, other meds, and even how your liver processes drugs can change how these targets respond. Diuretics can mess with electrolytes, which affects how well your blood clots. Acid reflux meds like proton pump inhibitors might interfere with how aspirin works. And if you’ve got kidney or liver problems, your body handles these drugs differently. That’s why a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work. What’s safe for one person could be dangerous for another, even if they’re both on the same medication.
What you’ll find below are real, practical breakdowns of how these targets interact with common drugs and supplements. You’ll see how fish oil and aspirin play together, why ranitidine got pulled from shelves, how diuretics shift your electrolytes, and why some blood pressure meds are better than others depending on your body’s needs. These aren’t theory-heavy articles—they’re clear, no-fluff guides written for people who want to understand what’s really happening inside their body, not just take a pill and hope for the best.
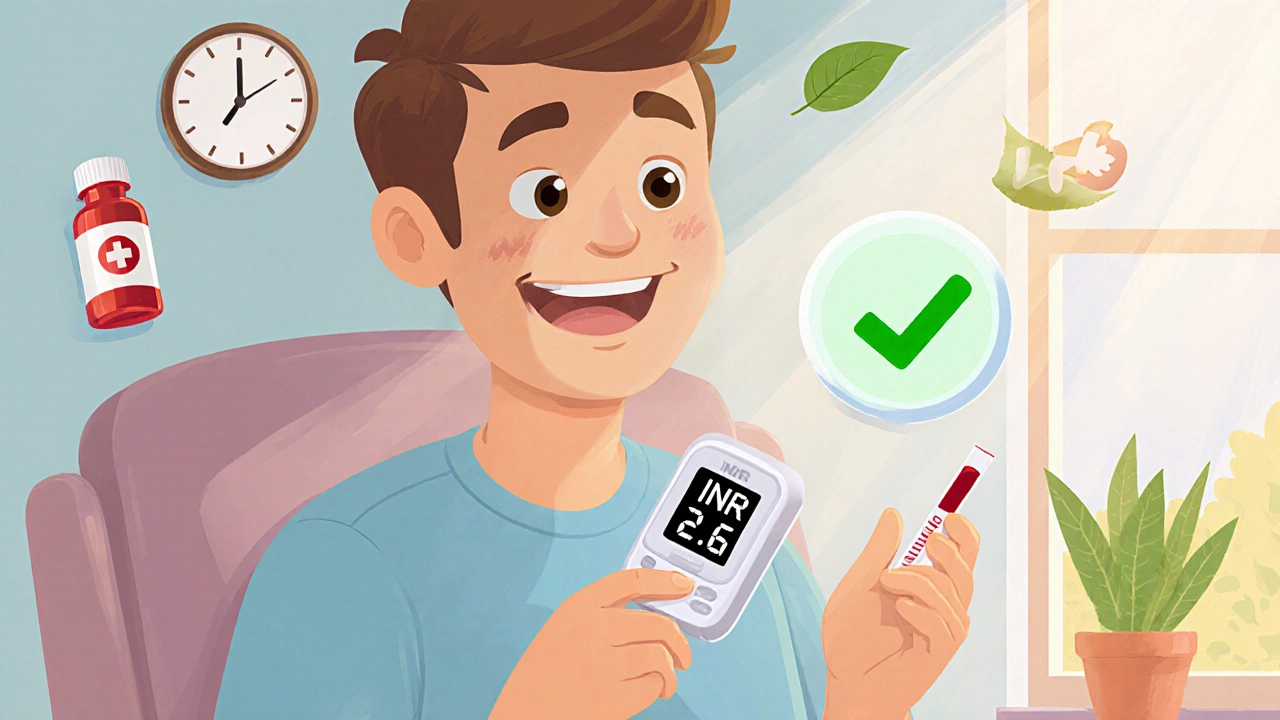

Monitoring Your INR: Understanding Blood Thinner Levels and Targets
Learn how INR monitoring keeps blood thinner levels safe and effective. Understand target ranges, home testing options, diet tips, and what to do if your numbers are too high or low.