Asthma Treatment: What Works, What to Avoid, and How to Stay in Control
When you have asthma treatment, a set of strategies and medications used to control breathing difficulties caused by inflamed and narrowed airways. Also known as asthma management, it’s not just about using an inhaler when you feel tight. It’s about knowing your body, spotting early warning signs, and staying ahead of flare-ups before they hit. Many people think asthma treatment means grabbing a rescue inhaler at the first wheeze—but that’s like putting out a fire after it’s already spread. The real goal is to keep the fire from starting in the first place.
Peak flow monitoring, a simple tool that measures how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. Also known as peak expiratory flow, it’s one of the most underused tools in asthma care. If you’re not tracking your peak flow daily, you’re flying blind. Your personal best number tells you when things are starting to go south—often days before symptoms get bad. That’s why doctors recommend it for everyone with moderate to severe asthma. And when you pair that with a clear asthma action plan, a personalized written guide that tells you exactly what to do when your symptoms change. Also known as asthma control plan, it turns confusion into confidence. Green zone? Keep doing what you’re doing. Yellow zone? Time to step up your meds. Red zone? Get help now. No guessing. No panic.
What most people miss is how much asthma triggers, environmental or physical factors that cause airway inflammation and breathing problems. Also known as asthma irritants, play a role beyond pollen and dust. Cold air. Exercise. Stress. Even strong perfumes or cleaning products. You can’t avoid all of them—but you can learn which ones hit you hardest. Keep a quick log for a week. Note what you were doing, where you were, and how you felt. You’ll spot patterns fast. And once you know your triggers, you can start making real changes: switching to fragrance-free laundry soap, wearing a scarf in winter, or keeping your bedroom dust-free.
And let’s talk about inhalers. Not all are the same. Some are for daily control. Others are for emergencies. Using the wrong one at the wrong time won’t help—and might make things worse. If you’re still using your rescue inhaler more than twice a week, your asthma isn’t under control. That’s not normal. That’s a sign you need to adjust your treatment, not just reach for more puffs.
There’s no magic cure. But there is a clear path: know your numbers, avoid your triggers, take your meds right, and act before things get bad. The posts below give you real, practical steps—how to use your peak flow meter correctly, how to read your asthma zones, which inhalers actually work for long-term control, and how to talk to your doctor when your current plan isn’t cutting it. No fluff. No theory. Just what works for people living with asthma every day.
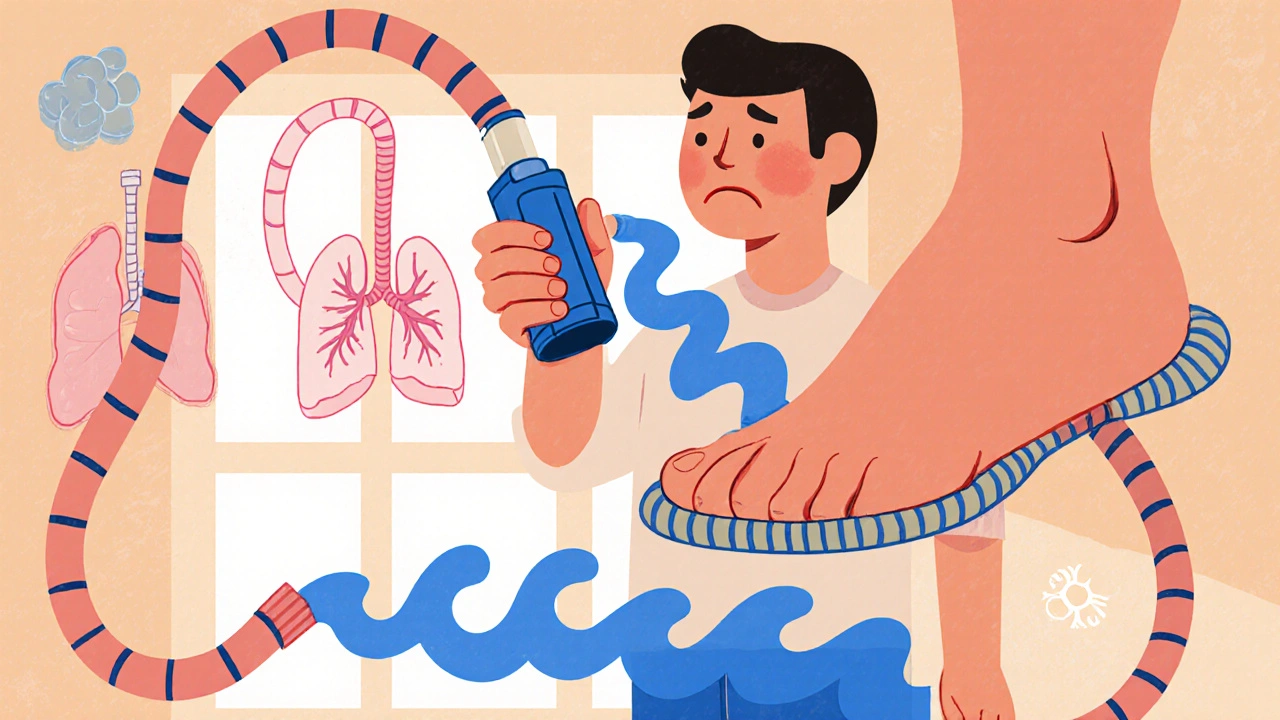

Bronchodilators and Corticosteroids: How Respiratory Medications Work
Bronchodilators open airways for quick relief; corticosteroids reduce inflammation for long-term control. Learn how they work together, why timing matters, and how to use them safely to manage asthma and COPD.