Anticoagulation Therapy: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
When your blood clots too easily, it can lead to strokes, heart attacks, or deadly pulmonary embolisms. That’s where anticoagulation therapy, a medical treatment designed to slow down blood clotting to prevent dangerous blockages. Also known as blood thinning treatment, it doesn’t actually make your blood thinner—it stops specific proteins from triggering clots. This isn’t optional for people with atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or artificial heart valves. Skip it, and you’re playing Russian roulette with your circulation.
Most people on anticoagulation therapy take warfarin, a long-used oral medication that blocks vitamin K to reduce clotting factors. But newer options like rivaroxaban or apixaban are now common—they don’t need constant blood tests and have fewer food interactions. Still, they all carry one big risk: bleeding. You can’t avoid it entirely. Brushing your teeth too hard, falling, or even taking fish oil or aspirin with your prescription can tip the scale. That’s why so many posts here focus on drug interactions, how common meds and supplements interfere with anticoagulants and increase bleeding chances. One person’s harmless supplement is another’s hospital visit.
It’s not just about the pills you take. Diuretics, painkillers, even some herbal remedies like St. John’s wort or ginkgo can mess with your therapy. And if you’ve got kidney or liver issues, your body handles these drugs differently. That’s why monitoring matters—your doctor isn’t just checking numbers, they’re watching for signs your body’s balance is shifting. You might not feel anything until you bleed internally. That’s why knowing your triggers is as important as taking your pill every day.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on how anticoagulation therapy intersects with everyday meds and supplements. From how warfarin interacts with fish oil to why ranitidine got pulled from shelves and what to use instead, these posts cut through the noise. You won’t find fluff here—just clear, practical info on what’s safe, what’s risky, and what you need to ask your doctor before you take anything new.
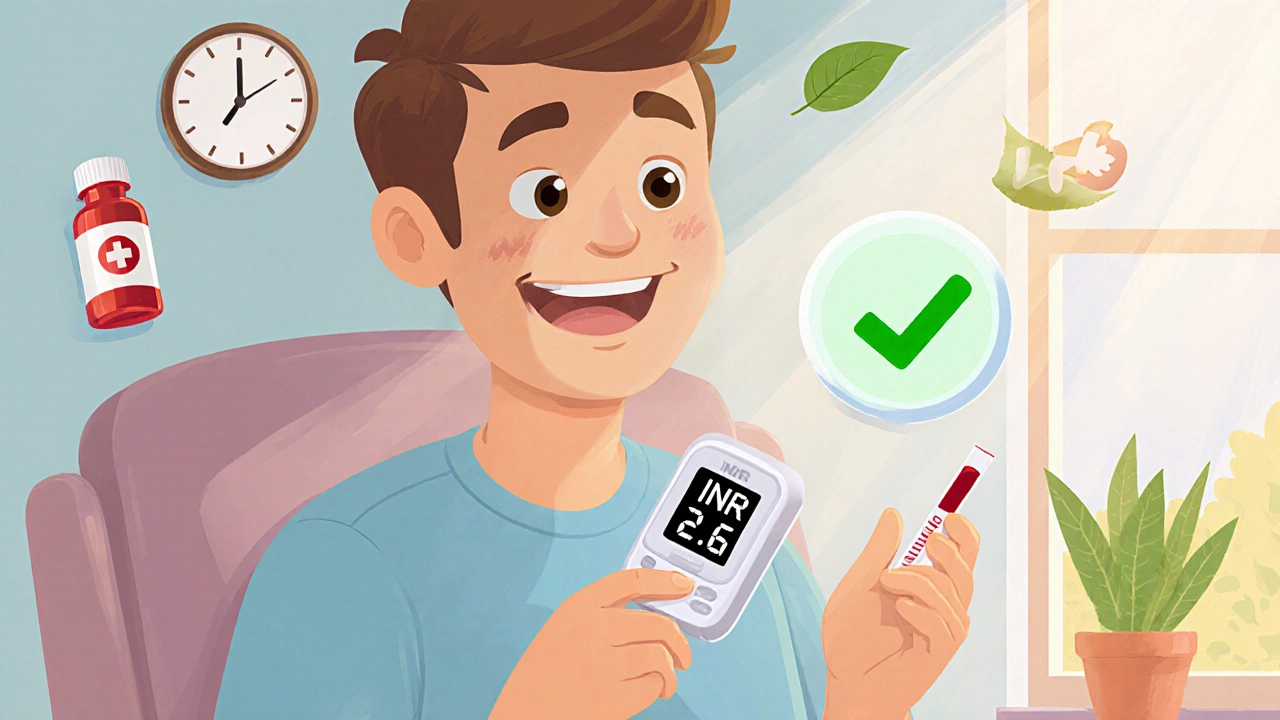

Monitoring Your INR: Understanding Blood Thinner Levels and Targets
Learn how INR monitoring keeps blood thinner levels safe and effective. Understand target ranges, home testing options, diet tips, and what to do if your numbers are too high or low.